Introduction
Genetic genealogy is changing the way people discover their roots. Instead of relying only on old records, photos, or family stories, people can now use DNA to uncover where they come from and how they are connected to others. This modern approach combines traditional research with science, making family discoveries faster, deeper, and often more accurate.
In countries like the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia, interest in DNA genealogy has grown rapidly. Millions of people are taking DNA tests to learn about their ancestors, find unknown relatives, or confirm long-held family stories. Immigration history, adoption cases, and multicultural societies have made DNA testing for ancestry especially popular in these regions.
What makes this method so powerful is its accessibility. You don’t need to be a professional historian or scientist. With one test and access to online tools, anyone can begin meaningful Family history research. In this guide, you’ll learn exactly how genetic genealogy works, the types of DNA tests available, and how people around the world are using it today.
What Is Genetic Genealogy?
Genetic genealogy is the study of family history using DNA evidence along with traditional genealogical records such as birth certificates, census data, and marriage records.
Traditional genealogy depends on documents and written sources. While valuable, records can be incomplete, damaged, or missing—especially for earlier generations. DNA genealogy fills these gaps by analyzing inherited genetic material passed down from your ancestors.
Traditional genealogy vs DNA-based genealogy
- Traditional research relies on paper records and oral history
- Genetic genealogy uses DNA to confirm biological relationships
- DNA can uncover connections where documents fail
- Both methods work best when combined
By merging records with DNA results, researchers can verify lineages, break through “brick walls,” and discover relatives they never knew existed.
How Genetic Genealogy Works
Understanding genetic genealogy is easier when broken into simple steps.
Step-by-step process
- Take a DNA test
You start with DNA testing for ancestry, usually through a saliva or cheek swab sample. - Lab analysis
The lab examines your DNA markers and compares them with millions of others. - Results and matches
You receive a list of DNA matches—people who share genetic segments with you. - Comparison with records
DNA data is combined with documents, trees, and historical information. - Building connections
Over time, relationships and ancestral lines become clearer.
Real-life use cases
- An adoptee in the USA finds biological parents
- A UK family confirms links to Scottish ancestors
- A Canadian discovers cousins across Europe
- An Australian traces Indigenous or immigrant heritage
These stories show how DNA genealogy transforms curiosity into meaningful discoveries.
Types of DNA Tests Used in Genetic Genealogy
Not all DNA tests serve the same purpose. Genetic genealogy commonly uses three main types of tests.
Autosomal DNA
The Autosomal DNA test is the most widely used and beginner-friendly option. It examines DNA inherited from both parents and works best for finding relatives within the last 5–7 generations.
Best for:
- Finding cousins and close relatives
- General Family history research
- Recent ancestral connections
Y-DNA
Y-DNA testing analyzes the Y chromosome, passed from father to son. It traces direct paternal lines and is used mainly by men.
Best for:
- Surname studies
- Deep paternal ancestry
- Male lineage confirmation
Mitochondrial DNA
mtDNA testing examines mitochondrial DNA passed from mother to child. It traces the direct maternal line for both men and women.
Best for:
- Maternal ancestry
- Ancient lineage tracing
- Confirming maternal relationships
Using the right test—or a combination—makes genetic genealogy more precise and meaningful.
How DNA Matches Help Build Family Trees
DNA matches are the heart of DNA genealogy. They show how people are biologically related.
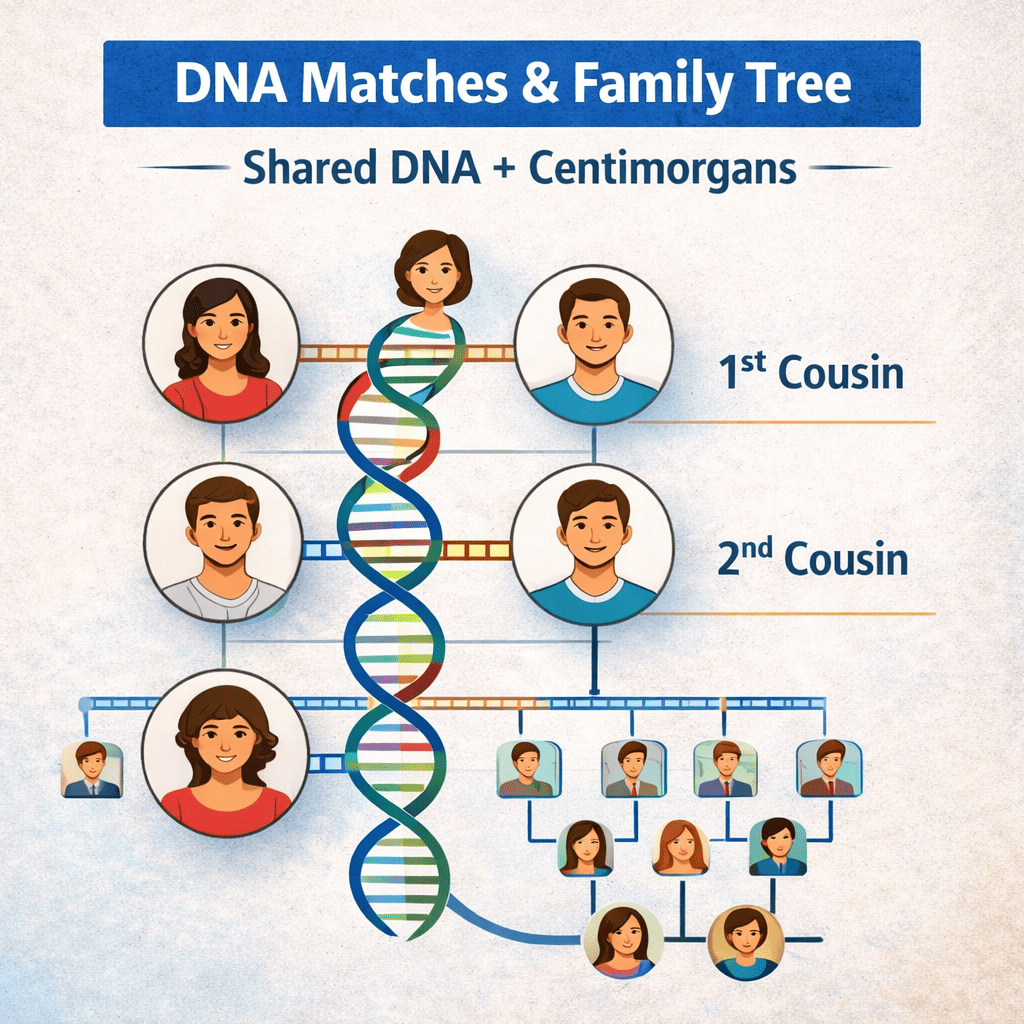
Shared DNA and centimorgans
- Shared DNA is measured in centimorgans (cM)
- More shared cM usually means a closer relationship
- Relationship predictions are estimates, not guarantees
By comparing shared segments, researchers can determine whether someone is likely a cousin, aunt, or distant relative.
Role of DNA databases
Large Genealogy DNA databases allow users to compare results with millions of others worldwide. These databases are especially valuable in the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia, where participation rates are high.
When combined with family trees and records, matches help extend ancestral lines backward and outward with confidence.
Popular Uses of Genetic Genealogy Today
The applications of genetic genealogy go far beyond curiosity.
Family history discovery
Many people begin Family history research to understand their roots, preserve stories, and pass knowledge to future generations.
Adoption and unknown parentage
DNA testing has helped thousands of adoptees and donor-conceived individuals reconnect with biological families using DNA genealogy tools.
Ethnicity and origins
An Ethnicity estimate provides a regional breakdown of ancestral origins. While estimates evolve as databases grow, they offer valuable insights into ancestral migration patterns.
Medical insights (basic overview)
Some people use DNA testing for ancestry to gain limited insight into inherited traits. However, genetic genealogy is not a replacement for medical testing or professional advice.
Benefits and Limitations of Genetic Genealogy
Like any research method, genetic genealogy has strengths and weaknesses.
Benefits
- Confirms biological relationships
- Breaks through missing records
- Connects relatives across countries
- Enhances traditional research accuracy
Limitations
- Results depend on database size
- Relationship predictions are estimates
- Privacy concerns require careful settings
- An Ethnicity estimate may change over time
Understanding these factors helps users approach DNA genealogy with realistic expectations.
Frequently Asked Questions (AEO Section)
What is genetic genealogy in simple terms?
Genetic genealogy uses DNA testing to discover family relationships and ancestral origins by comparing your DNA with others.
Is genetic genealogy accurate?
DNA genealogy is highly accurate for identifying biological relationships, but relationship predictions and ethnicity results are estimates that improve over time.
How long does DNA genealogy testing take?
Most Ancestry DNA test results are available within 4–8 weeks, depending on the provider and location.
Is DNA testing safe and private?
Reputable companies allow users to control privacy settings. Reading terms carefully is essential before sharing data in Genealogy DNA databases.
Conclusion: Start Your Genealogy Journey Today
Genetic genealogy has opened doors that were once closed to traditional research alone. By combining science with history, people across the USA, UK, Canada, and Australia are discovering relatives, confirming stories, and understanding their origins in powerful ways.
Whether you’re curious about your roots, building a family tree, or reconnecting lost branches, DNA genealogy offers tools that were unimaginable just a generation ago. Start small, stay curious, and use DNA responsibly.
👉 Ready to explore your past? Begin your journey with DNA testing for ancestry and see where your story truly begins.
